Meiosis (or Gametogenesis)
COMPARING FEMALE and MALE MEIOSIS (GAMETOGENESIS).
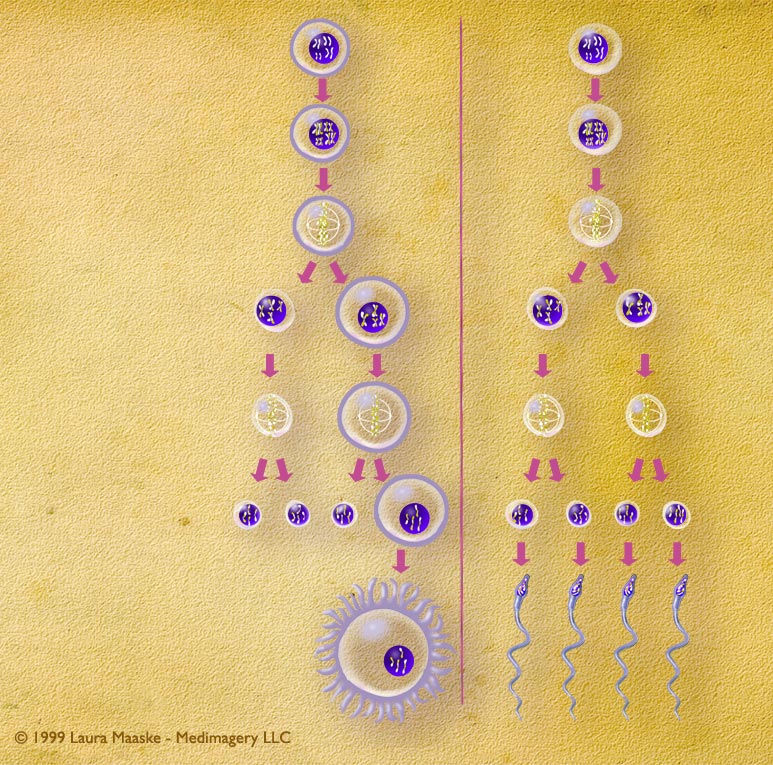
Cell division of female and male gametes and their successive cell divisions.
Meiosis is a word that comes from the Greek word, "meioun", which means to lessen. Biologically, meiosis, also called gametogenesis, is the process of reducing cells to half their chromosomal size: for humans this means cutting their chromosal humber down from 46 to 23. A cell which has had its chromosome number reduced to half is called a "haploid" cell. The purpose of meiosis is to prepare a cell that will be capable of sexual reproduction: able to combine with another haploid cell to make a new organism.
Below is a comparison of the steps involved in female and male meiosis (or gametogenesis). Note the important difference. Female gamete development produces a single primary oocyte as the final product from the four original primary oocytes. Male gamete development produces four spermatazoa from the original primary spermatazoa.
| Female Meiosis (Oogenesis) |
Male Meiosis (Spermatogenesis) |
|---|---|
| Before meiosis I (a process called Interphase), the spermatogonium's 46 single chromosomes are replicated to form 46 pairs of sister chromatids, which then exchange their genetic material through synapsis so that none of the chromosomes resemle the original chromosome arrangements. Each one is unique from the parent cell and from one another. | (same) |
| The first meiotic division - Meiosis I. The two cells divide to produce four cells. Each of the four cells contains 46 chromosomes, the pairs of which were broken in division. | (same) |
| The second meiotic division - Meiosis II. The second division leads to the production of one ovum, or egg cell, from each primary oocyte. Of the four daughter cells that are produced when the first primary oocyte divides, three come out much smaller than the fourth. These highly reduced cells, each of which contain 23 chromosomes, are called polar bodies. The polar bodies disintegrate. One large ovum is left as the final product of oogenesis, which holds all the nutrients and and added intracellular materials from the reduced cells. | The second meiotic division - Meiosis II. The two daughter cells go through a second division to yield four cells containing a unique set of 23 single chromosomes that ultimately mature into four sperm cells. Four sperm are generated from every spermatogonium. |
| forms 1 egg | forms 4 spermatozoa |
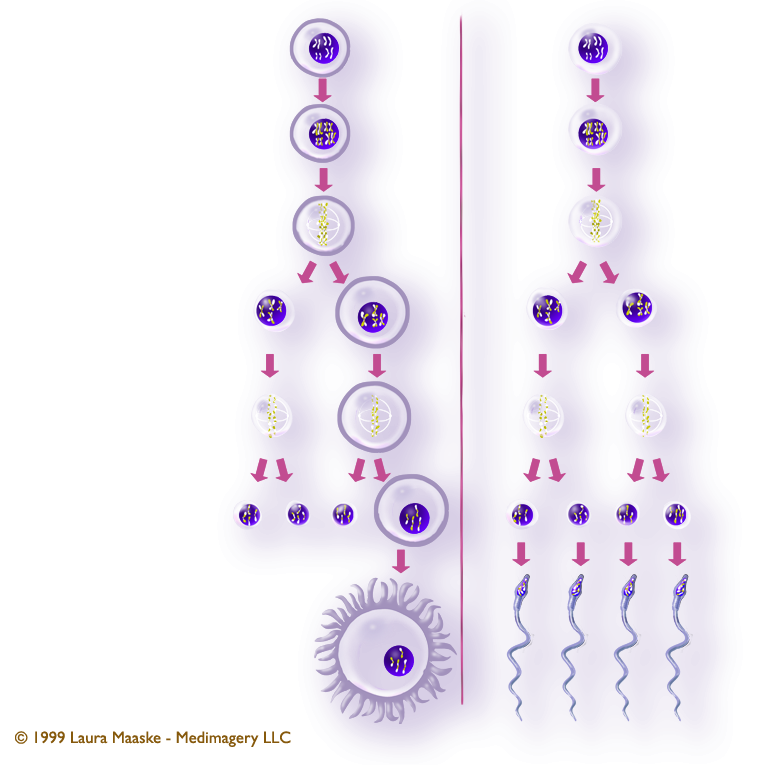
Comments: This illustration was prepared for a human physiology exhibit at The Cleveland Art Museum to illustrate the differences in the development of male and female gemetes.
Audience: Cleveland Art Museum human physiology display.
Medium: Developed digitally using Illustrator and Photoshop.
Laura Maaske, B.Sc., M.Sc.BMC
Racine, WI 53402
Cell: (262) 308-1300
Contact Laura
Text Copyright © Medimagery - Laura Maaske LLC
Illustration Copyright © 1999 Laura Maaske - Medimagery LLC.
Return to meiosis illustration..
Also related to this topic is the Fetus, engaged position illustration.